Understanding Hearing Aids
Hearing aids are small electronic devices that can be worn in or behind the ear. They amplify sound, making it easier for people with hearing loss to listen, communicate, and participate more fully in daily activities. These devices vary in price, size, special features, and the way they’re placed in your ear.
Types of Hearing Aids
Various types of hearing aids cater to different preferences and hearing loss needs. The primary types include:
- Behind-the-Ear (BTE): Houses the electronic components in a case that rests behind the ear, delivering sound into the ear canal via a tube and earmold.
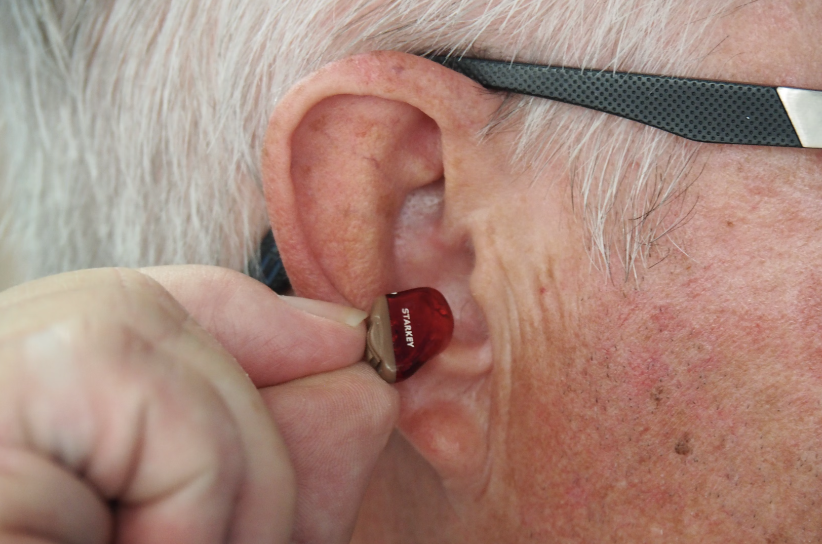
- In-the-Ear (ITE): Custom-made devices that fit within the outer portion of the ear, suitable for mild to severe hearing loss.
- In-the-Canal (ITC) and Completely-in-Canal (CIC): Smaller devices that fit partially or completely in the ear canal, making them less noticeable and ideal for adults with mild to moderate hearing loss.
- Receiver-in-Canal (RIC): Similar to BTE but with the speaker or receiver placed inside the ear canal, offering a more natural sound quality.
Features of Modern Hearing Aids
Modern hearing aids come equipped with various features to enhance user experience:
- Directional Microphones: These microphones help focus on sounds coming from a specific direction, improving the ability to hear in noisy environments.
- Rechargeable Batteries: Convenient and cost-effective, eliminating the need for frequent battery replacement.
- Telecoils: Make it easier to hear when talking on a telecoil-compatible telephone and in public facilities equipped with induction loop systems.
- Wireless Connectivity: Allows direct connection to smartphones, TVs, and other devices for improved sound quality.
- Noise Reduction: Reduces background noise for clearer listening in noisy environments.
Selecting the Right Hearing Aid
Choosing the right hearing aid is a critical decision that involves several considerations:
- Hearing Test: An audiologist will conduct a hearing test to determine the type and extent of hearing loss.
- Lifestyle Considerations: Consider your daily activities and environments to determine the best fit and features.
- Aesthetic Preferences: Hearing aids come in various sizes and styles; some are more discreet, while others are more noticeable.
- Budget: Prices vary, so it’s important to consider what features are essential and what might be optional.
- Trial Period: Many providers offer a trial period to test the hearing aids in your everyday environment.
Adjusting to Hearing Aids
Adjusting to hearing aids takes time and patience:
- Gradual Introduction: Begin by wearing them for a few hours each day, gradually increasing the duration as you become accustomed to them.
- Practice in Different Environments: Use them in various settings to get used to different soundscapes.
- Regular Adjustments: Follow-up appointments with your audiologist are crucial for making necessary adjustments and ensuring comfort.
Maintenance and Care
Proper care and maintenance are key to the longevity and performance of your hearing aids:
- Daily Cleaning: Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for cleaning and maintenance to prevent earwax and moisture buildup.
- Proper Storage: When not in use, store them in a dry, cool place, preferably in a dehumidifier box.
- Regular Check-Ups: Visit your audiologist regularly for professional cleaning and check-up.
Overcoming Stigma and Building Confidence
While some people may feel self-conscious about wearing hearing aids, it’s important to focus on the significant benefits they bring. Embrace the improvement in hearing as a positive change and educate others about how the devices help.
The Future of Hearing Aids
Technological advancements continue to revolutionize hearing aids, with future developments focusing on enhanced sound quality, further miniaturization, and integration with a range of digital devices. Innovations in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning algorithms are expected to create more personalized and adaptive hearing experiences.
Conclusion
Hearing aids are a vital tool for individuals with hearing loss, offering the chance to improve communication, engage more fully in activities, and enhance overall quality of life. By understanding the types of hearing aids, their features, and how to care for them, users can maximize the benefits these devices provide. With the right approach and ongoing support from audiologists, hearing aids can significantly enhance the auditory experience, allowing users